06/08/2010
RNA extraction (2nd attempt)
- Using tissues sampled for proteins extraction stored at -80°C
- Weigh-in 50-100 mg (according to the manufacturer's protocol !)
- Trizol extraction
- Resuspension in 100 µl DEPC-H2O
- Storage at -80°C
Reverse transcription
- 17,5 µl of RNA
- 70°C, 5min
- Transfer on ice 5-10 min
- Add 7.5 µl of Master Mix containing :
- 5 µl MMLV Buffer 5X
- 1,25 µl dNTPs 10mM
- 0,5 µl MMLV RTase
- 0,5 µl oligo dT primer
- 37°C, 1h
- 95°C, 3min
- Storage cDNA in the freezer
qPCR
Samples from the same treatment were pooled : 2 µl of each individuals/4 treatments (H, V, HV, C)
Test of the 5 pairs of primers available in the lab and designed for A. elegantissima (S. Roberts) : VWR, bactin, SOD, S1PP2, PSAP
1 µl of each "treatment" + 2 negative controls /set of primers
Master mix for each pair of primers (Volume t : 25 µl)
- 2X SyBr Green MM : 12,5 µl
- BSA : 1,5 µl
- Forward primer : 0,5 µl
- Reverse primer : 0,5 µl
- sterile H20 : 9 µl
Annealing Temperature : 55°C
05/08/2010
Anemone project -> see Anemones page
Preliminary study
- Pellet 5ml (5x1ml) of the Vt culture (growth ON), resuspend in 250 µl
- Treatments :
- 2nd treatment : Vt inoculation-3h
- 3rd treatment : Vt inoculation+Heat Stress (35°C) - 3h
- RNA extraction using Trizol protocol
-> we used too much tissues -> failure !
04/08/2010
Anemone project -> see Anemones page
Preliminary study
- Set up of the experiment : 4 individuals/treatment (=4x3), 3 control.
SWT = 12-15°C
Weigh-in of each individual
Control of the temperature for the Heat Stress treatment with a thermometer in a separated dish containing SW in the hot bath.
- 1st treatment : Heat stress 35°C-3h
- Pictures, weigh-in after treatment and sampling of tentacles for RNA & proteins -> store at -80°C
03/08/2010
Differential Display
Goal : assess differences in gene expression between treatments with regular PCR using arbitrary primers.
After the PCR, run a gel and see if the amplification worked (not sure because arbitrary primers were chosen) and if possible, observe different patterns of expression.
Cut the band and sequence.
On Gorgonia ventalina samples, cDNA prepared in Cornell Univ. 3 samples : control, injected with SPX, injected with Aspergillus
Using 2 pair of primers (1 arbitrary primer : A17, 1 specific to the adaptor)
Regular PCR (3 samples + 2 control-)
02/08/2010
Serum Agglutination Test
On a 2 wells slide :
- control : 50 µl sterile SW + 25 µl culture Vibrio tubiashii
- sample : 25 µl sterile SW + 25 µl culture + 25 µl polyclonal Ab (specific to Vt)
Observation under microscope 10X :
- control : no agglutination (like stars in the sky)
- sample : agglutination (like snow flakes) -> antibody clumps Vt together
31/07/2010
3rd gel : Magic !
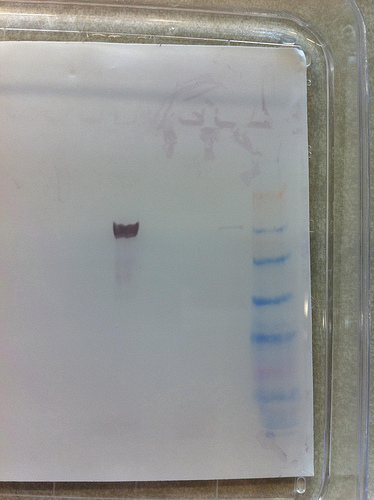 Thanks Steven !
Thanks Steven !Strong signal for barnacle, small signal for oyster.
No signal for both anemones.
The Barnacle sample can be used as a positive control for further experiment (we can load less)
Heat stress barnacles
Heat stress 35°C-ON.
Same procedure to process the samples for further protein extraction.
Weight : 0.02g
Field trip : Cattle point - collecting anemones
Sampling of Anthopleura elegantissima individuals in tide pools for the group project.
5 individuals collected in sterile falcon tubes for mucus analysis (Morgan & Kathy)
12 indivuals collected in a plastic bag.
Back to the lab : The anemones were placed in glass dishes in a clean tank.
Oyster larvae feeding and water change
Class project :
Changing of the water in each "bottle" tank : filtering the water with a 70 µm filter. Rinse the bottle.
Sampling each bottle for further counting of dead/alive larvae.
Filling up the bottle and rinse the filter with filtered SW.
Feeding the larvae with 25ml of algae.
30/07/2010
Western Blot, 2nd attempt
Steven Roberts loaded a gel and western with oyster gill (supposed to work with the antibody), crab and littorina samples.
--> one band for the oyster sample : the antibody works
Field trip
To Argyle creek
Sampling of Mopalia (chitons) potentially diseased. No visible signs of diseases.
-> Sampling of "presumed diseased" individuals which come off the rock easily, and "healthy" ones well attached.
Heat stress experiment / 3rd gel
Proteins extraction of:
- Anthopleura tentacles as suggested in Snyder & Rossi_2004
- Metridium's acontias
- Barnacles sampled at low tide, on the sun. The antibody is supposed to bind very well with barnacle.
Weight : 0.08g
Sample : control before heat stress
- Oyster as positive control
Other barnacles are heat stressed at 35°C in the water bath.
5 barnacles sampled after 3h of heat stress. Weight : 0.02g. Added to 0.5 ml of CellLytic Solution, homogenized, pellet. Supernatant transfered in a new tube. Both tubes stored at -20°C
29/06/2010
Protein -2
Gels from the day before : verification on the appropriate concentration.
Run another gel for Western Blot
45min-150V
Western Blot
Using`the WesternBreeze Chromogenic Western Blot Immunodetection Kit (Invitrogen)
And an anti-Hsp70 antibody (known to work on oysters).
-> No bands on the membrane (no magic !)
Ponceau stain to check the presence of proteins on the membrane (stains in red/pink) --> no stain
Possible explanations : - mistakes during the experiment
- No binding of the anti-hsp70 on anemones
- No expression of those proteins on the samples
- Amount of proteins in the samples to low
According to Snyder & Rossi_2004_Stress Protein (HSP70 family) expression in intertidal benthic organisms: the benthic organisms: the example of Anthopleura elegantissima (Cnidaria: Anthozoa)_Sci. mar., 68 (1) : 155-162, we might have taken too much tissues form the anemones body which may have "dilute" the proteins. The HSP seem to be expressed (almost only) in the tentacles.
Oyster dissection - Hemolymph microscopy
Look for Bonamia in Ostrea edulis (ordered)
After opening the oyster, take a hemolymph sample from the heart (really small round shape attached to dark brown ventricles) with a syringe. Loni and me weren't able to suck any liquid from the heart, so we dabed it with a kimwipe and we gently dabed it on a slide.
We also dabed the digestive glands on another slide.
Methanol 1 min
Giemsa stain ~2min, rinse in H20.
Observation : Hemocytes appear to be normal, no Bonamia.
28/07/2010
ISH-3
- From Detection-step 7
Bismarck Brown Y : stains acid mucins to yellow color
Increasing ethanol concentration : dehydratation
- Observation : No stain... Possibilites : no binding to the probe (no target), mistake made during the experiment
We still can see rickettsia ovale shape inclusions in the epithelial tissue
- Observation of a H&E (Hematocylin colors nuclei in blue, Eosin colors the rest in pink/red) stained slide : rickettsia = dark brown/purple circles (tissue = pink)
Protein extraction
From anemones Anthopleura elegantissima heated (stressed) ON ~25°C.
Weight tissue = 0.02g
Using the CelLytic Mammalian Tissue Lysis/Extraction Reagent (Sigma)
Following this protocol
SDS-PAGE using Precise Protein Gels (Thermo Scientific)
Loading of 3 different volume of each samples to optimize the amount of proteins
Migration : 45min-150 V
Comassie Stain
Destaining in 10% acetic acid ON
27/07/2010
ISH-2
- Stringency washes
Triton X-100 : detergent
Blocking Buffer : decrease the back- ground by saturing non-specific binding sites
- Detection of the probe up to step 6 (nothing after 15min -> incubation ON)
Anti-DIG : binding to the probe (UTP-DIG)
NBT (nitroblue tetrazolium) : oxidant
BCIP (5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl phosphate) : Phosphatase alkaline substrate which is dephosphorylated by the PA and then dimerizes -> this dimer reduces NBT to form an insoluble dark blue/purple diformazan precipitate
26/07/2010
ISH : Withering syndrom on abalone (=Syndrome du dépérissement)
--> specific probe for the "classic" Rickettsia were designed. Test on "stifled" and "new" rickettsia identified in histology to see if it's the same bacteria causing different histological symptoms or if it's another strain.
Following the protocol http://bio533.wikispaces.com/Lab_Withering
(Probes and solutions were prepared on the 24/07 by Lisa C.)
NB : It is important to accomodate the tissues to every new solutions which might cause osmotic/ionic shock. Accomodation with pre-buffer (or graded concentrations series) before each step containing a new solution.
- Tissue deparaffinization
- Rehydratation of tissues with a graded ethanol series (end by Tris Buffer for tissues acclimatization)
- Permeabilization of tissues
PBS (Phosphate Buffered Saline)
- Prehybridization using the "alternative" prehyb. buffer.
SSC : citrate buffer, increase the ionic force and facilitate hybridization
-> SSC+formamide : increase stringency, facilitate hybridization
DEPC H20 (diethypyrocarbonate) : decontamination -> RNAse free water
- Hybridization of the probe on the target sequence_ON-53°C-humid chamber
23/07/2010
Plates observation : 48h
| Sample |
MA2216 |
TCBS |
|---|---|---|
| Water |
Ø |
Ø |
| L1 |
= 22/07 |
- new little, round, light green, bright colonies -> contamination ? water in the plate... - several yellow, round, bright - 1 grey-green, central blue-green spot |
| L2 |
= 22/07 |
- several yellow, round, bright - 1 big yellow, grainy, indented - 1 small bright green |
-> need to re-streak colonies on new plates.
Use a hand-made grid to isolate and identify colonies.
MA2216 : Isolation of 15-20 colonies for each duplicate (L1, L2)
TCBS : Isolation of every isolated colonies
Reverse transcription
Protocol :
- 17,75 µl of RNA in a sterile microtube
- 70°C, 5min
- Transfer on ice 5-10 min
- Add 7.25 µl of Master Mix containing :
- 5 µl MMLV Buffer 5X
- 1,25 µl dNTPs 10mM
- 0,5 µl MMLV RTase
- 0,5 µl oligo dT primer
- 42°C, 1h
- 95°C, 3min (the heather was actually on 85°C, so 3 more minutes in "real" 95°C)
- Storage cDNA in the fridge (4°C)
QPCR
2 genes : - gene of interest : c-jun N-terminal kinase
- reference (control) : actin
Master mix (1/set of primers)
- 2X SyBr Green MM : 12,5 µl
- BSA : 1,5 µl
- Forward primer : 0,5 µl
- Reverse primer : 0,5 µl
- sterile H20 : 8 µl
- template cDNA : 2 µl
2 duplicates for each set of primers
2 negative control (no template, only water) for each set
NB : We actually used nanodrop water, which is not sterile... -> contamination ?
well :
| Well |
D1 |
D2 |
D3 |
D4 |
D5 |
D6 |
D7 |
D8 |
| Sample ID |
ETSO3 |
ETSO3 |
T- |
T- |
ETSO3 |
ETSO3 |
T- |
T- |
| C jun K |
actin |
|||||||
QPCR Program :

22/07/2010
Observation des boîtes de culture du 21/07
| Echantillon |
MA2216 |
TCBS |
|---|---|---|
| Eau |
Ø |
Ø |
| L1 |
plusieurs col. blanches, brillantes, lisses, rondes |
- jaunes poussin, lisses, brillantes, rondes - 1 verte claire, opaque, ronde |
| L2 |
idem |
idem (+ de vertes) |
Extraction ARN (échantillons préparés le 20/07, conservés sur carboglace à -20°C)
Sur glace : homogénéisation des tissus avec un piston stérile
- Ajout 1 ml Trizol - Mix
- RT - 5 min (dissociatio complète des complexes nucléo-protéiques)
- Ajout 200 µl Chloroforme (ou BCP, 1-bromo-3-chloropropane) - Mix
- RT - 15 min
- Centri, 14000g - 15 min - 4°C -> 3 phases : phase aqueuse = ARN, interphase et phase organique (rouge)= ADN, protéines
- Récupérer le surnageant et ajouter 500 µl d'isopropanol - Mix
- RT - 5'
- Centri. 14000g - 8 min - 4°C
- Lavage : Ajout 1 ml éthanol 75% (dilué dans Eau DEPC) - Resuspendre
- Centri. 14000g - 5 min
- Eliminer tout l'éthanol - Bref spin
NB : le culot peut être invisible...
- Eliminer le reste d'éthanol, laisser sécher (pas trop).
- Resuspendre dans de l'eau DEPC (quantité dépend de la taille du culot). Ici, 200µl.
Si difficultés à resuspendre, chauffer à 55-60°C.
Culot très difficile à resuspendre -> Prélèvement de tout le surnageant en supposant qu'il contient assez d'ARN, conservation du culot et du surnageant au cas où, sur carboglace à -20°C.
Dosage impossible car pas de nanodrop dans le labo.
21/07/2010
Armina disease diagnostic
Armina sp. (nudibranch) specimens sampled in Tacoma (South Seattle) showing symptoms of an unknown disease -> diagnostic test.
Symptoms = epidermic disorder, modificication of the dorsal stripe pattern, unusual behaviour (lay on the back), quick death.
Preliminary diagnostic of diseased individuals ("Disease" tank), healthy individuals and recently affected indivuals ("Healthy" tank).
-> Dis-Health-1 (Diseased indivual from the supposed "healthy" tank).
~5cm long
~40% of the body affected
2 types of lesions : 1 big white (Marie), Several orange lesions (Loni).
Non-lesion sites streaked by Matthew and Sarah
Method :
SwabbedStreaked on duplicate TCBS Agar (Difco™) and MA2216 (Difco™) plates : L1, L2 ML
Control plates : Water from the "healthy" tank on each type of plate.
-> RT, ON
Gram-staining of lesion and non-lesion sites (Carolyn).
-> Gram - : pink
Gram + : purple
DNA extraction Littorina samples
Sample ID : ETSO3, Littorina sitkana (Emma)
Weight : 0,02 g
Using the Stool Kit Qiagen according to the manufacturer's instructions. See : http://www.qiagen.com/products/genomicdnastabilizationpurification/qiaampsystem/qiaampdnastoolminikit.aspx#Tabs=t1
QIAamp_DNA_Stool_Handbook.pdf
NB : Leak at step 16. Loss of ~30% of the solutions...
Stored at 20°C
PCR
PCR Mix :

27F sequence : 5’-(A)GAGTTTGATCMTGGCTCAG-3’, Tm=56,3°C (55,6°C)
1492R sequence : 5’-GGTTACCTTGTTACGACTT-3’, Tm=52,4°C
PCR Program :

20/07/2010 : Field Sampling
Cattle point (SE of San Juan Island)
Collecting Littorina sitkana and Littorina scutulata at low tide (biggest individuals).
Histology slides
- Abalone (normal) : observation of the oesophagus, pieces of radula, foot muscle (geometrical fibres), nerves
- Flat oyster infected by Bonamia (protozoa parasite) : observation of intestin (typical shape), stomach, hermaphroditic gonad, hematocytes.
Prep. Littorina +/- trematode for DNA and RNA extraction
1)
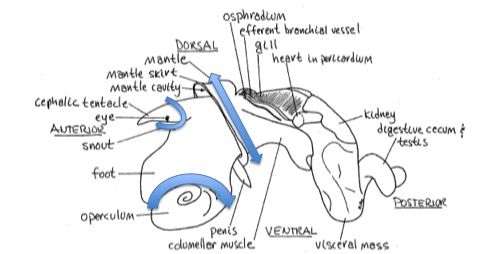 Crack shell, remove shell fragments
Crack shell, remove shell fragments2) Remove : head, operculum, digestive gland
3) Save a small slice of foot (on operculum) for DNA extraction (storage -20°C) samples ID :ML1-6 D
4) Save the rest of the foot for RNA extraction (storage dry ice -20°C) samples ID : ML1-6 R (blue RNase free microtubes)
5) Cut off the digestive gland (DG) and observe it under the dissecting scope for moving trematodes
3 x Littorina sitkana (ML 1-3)
3 x Littorina scutulata (ML 4-6)
No infected samples.
http://webs.lander.edu/rsfox/invertebrates/littorina.html
19/07/2010 : Invertebrates anatomy
Dissection : Sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus (Stimpson, 1857) - similar to Paracentrotus lividus, Mediterranean black sea urchin-
Apparently healthy (no visible signs of lesions)
1) Oral side down. Cut through the circumference of the urchin with sharp scissors
NB : Be careful not to cut too deep into the body cavity to avoid cutting internal organs.
2) Carefully separate the two halves
3) Observation of the digestive system, gonads
Reminder : http://webs.lander.edu/rsfox/invertebrates/